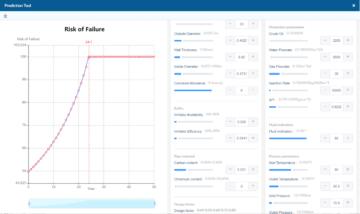
SMARTCORR® Corrosion and Erosion Management System (SCEMS)
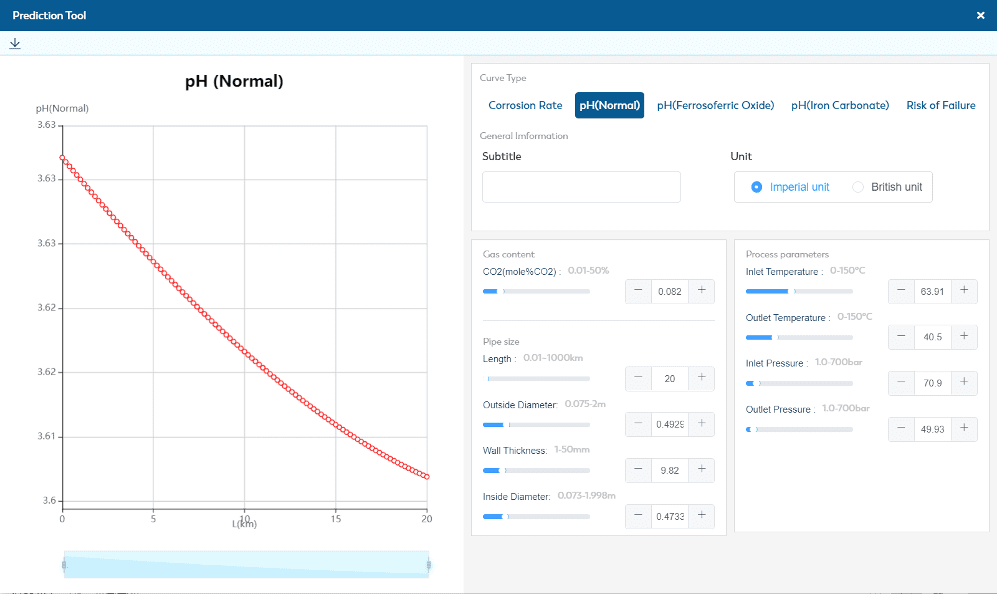
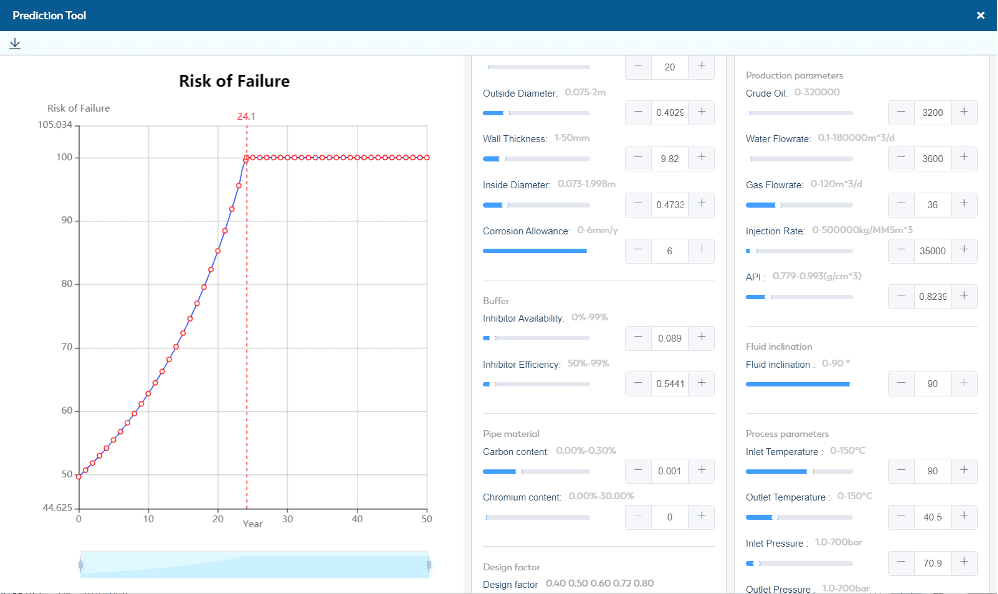
Corrosion management software connects to a network of sensors inside pipes, tanks and other vessels to help predict failures before leaks can develop. An erosion and corrosion monitoring system measures the thicknesses of this infrastructure and alerts operators to metal loss that could lead to failures and costly downtime. Because oil and gas companies operate in highly corrosive environments, they need to prepared for conditions that will impact their equipment and infrastructure on a regular basis.
With the costs of corrosion estimated to exceed over $60 billion globally ignoring the problem is not an option for those that want to maintain optimal opex. . The SCEMS corrosion-analysis software from SMARTCORR® provides a crucial tool for collecting and analyzing pipeline data to prevent these catastrophic and unnecessary costs.